Brain farts or something else? Telltale signs of inflammation in the brain, and 4 foods to fight it
02/01/2018 / By Michelle Simmons

Inflammation is known to play a role in the development of a lot of ailments and long-term health conditions — and the brain is not immune to it. Inflammation in the brain, whether acute or chronic, can cause serious health problems. Because brain inflammation is a silent killer, you must be aware of its telltale signs. You may have inflammation in the brain if you experience one or more of the following:
- Slow mental processing or a foggy feeling in the brain;
- Over fatigue or constantly needing caffeine to feel awake;
- Inability to focus or a short attention span; or
- Strong reactions to environmental allergens or toxins, such as artificial perfume, secondhand smoke, pollution, or other chemical smells.
Furthermore, chronic inflammation in the brain is also associated with one or more other health conditions. These include:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Anxiety
- Dementia
- Depression
- Diabetes
- Metabolic syndrome or pre-diabetes
- Mood disorders
- Multiple sclerosis
- Parkinson’s disease
- Stroke
- Schizophrenia
Meanwhile, the exact cause of brain inflammation or encephalitis remains unknown. However, it is most commonly associated with a viral infection. The common viruses that can cause brain inflammation include herpes simplex virus, enteroviruses, mosquito-borne viruses, tick-borne viruses, rabies virus, and childhood infections. In addition, bacterial infections and noninfectious inflammatory conditions can also cause brain inflammation. This condition can occur in anyone, but an increased risk can be seen in young children and older adults and people with HIV/AIDS or those with a weakened immune system. The possibility of developing the condition also depend on geographical regions and season of the year.
Four foods to fight brain inflammation
Fortunately, inflammation in the brain can be prevented with four foods by nourishing the brain and reducing inflammation. (Related: Pomegranates reduce brain inflammation, helping protect against Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and neurological disease.)
- Grass-fed butter – Grass-fed butter is a type of butter that is rich in fats and butyric acid — a nutrient that can help to decrease glucose and reverse inflammatory damage from high levels. However, you must be careful when selecting butter. Make sure that it is grass-fed and of high quality because conventional butter does not have the same fatty acid contents.
- Avocado – Avocado is a known superfood because it is not only rich in healthy fats, but also in various vitamins and minerals. It has monounsaturated fats that can help restrain and balance oxidized cholesterol, which is an inflammatory marker that can be linked with brain inflammation and other health risks such as stroke and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Coconut oil – Coconut oil is another superfood that contains medium chain fatty acid that can be transformed by the liver into ketones for fuel. Consuming coconut oil can be beneficial to the brain as it can lessen inflammation. Moreover, it can help lower insulin and reduce body fat as well as aid in weight loss.
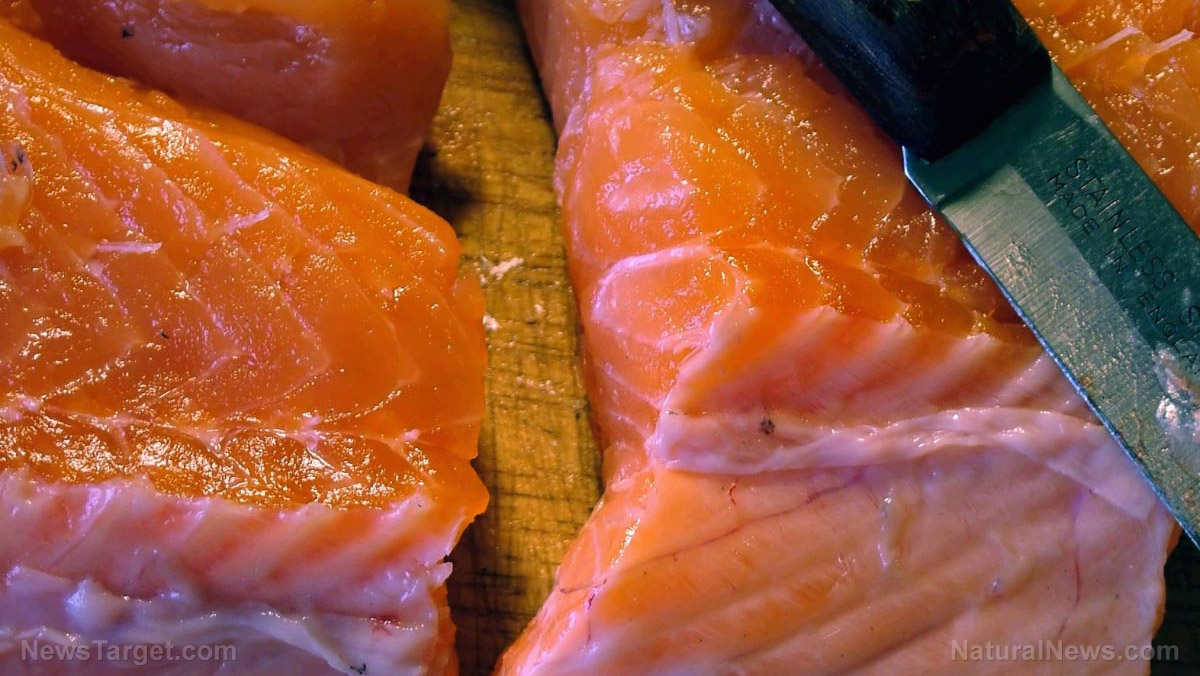
- Salmon – Salmon has the greatest levels of omega-3 fatty acids compared to other fish varieties. Omega-3 fatty acids are known to contain strong anti-inflammatory properties. Thus, the consumption of high quality salmon and other fatty fish can slow down cognitive decline and decrease the signs of aging. In turn, these can make or keep the brain healthy.
Read more stories about the brain and how to keep it healthy at Brain.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under:
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 SUPERFOODS NEWS