Fight inflammation with the help of these 6 powerful vitamins
11/26/2020 / By Divina Ramirez

Inflammation is a key immune response to infection or injury. It means that immune cells are actively helping the body to heal. But inflammation that persists could be a sign of an underlying health problem.
If the body is in a state of chronic inflammation, it is unable to heal properly. Over time, chronic inflammation could lead to serious conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, arthritis and cancer.
Fortunately, certain vitamins can help reduce inflammation and decrease the risk of chronic disease. These vitamins include:
Vitamin A
Vitamin A helps protect cells from oxidative stress and inflammation caused by unstable molecules called free radicals. According to several studies, vitamin A plays an important role in innate and acquired immunity, as well as in the body’s response to inflammation. (Related: Cannabis shows great promise for treating chronic inflammation and pain.)
Vitamin A can be found in abundance in the following foods:
- Carrots
- Dandelion
- Kale
- Collard greens
- Spinach
- Pumpkin
- Bell peppers
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that neutralizes harmful free radicals responsible for inflammation. Vitamin C also contributes to immune defense by supporting cellular functions that are crucial for innate and adaptive immunity.
In addition, Vitamin C is known to lower levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) in the blood. The liver produces CRP when inflammation is present. Elevated levels of CRP are common in people with inflammatory conditions.
These are the best dietary sources of vitamin C:
- Orange
- Grapefruit
- Broccoli
- Bell pepper
- Brussels sprouts
- Tomato
- Cantaloupe
- Cabbage
- Potato
- Spinach
Vitamin D
Vitamin D helps protect cells from the harmful effects of chronic inflammation by regulating the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. These signaling proteins are involved in the pathogenesis of many diseases, including arthritis, asthma, diabetes and cancer.
In fact, a 2012 report showed that low levels of vitamin D failed to inhibit inflammation, whereas high levels of the nutrient were able to do so. This suggests that patients with arthritis, asthma and other inflammatory conditions can benefit from vitamin D supplementation.
When skin is exposed to sunlight, it produces vitamin D from cholesterol. But vitamin D can also be found in a wide range of foods, including:
- Trout
- Tuna
- Egg
- Salmon
- Sardine
- Beef liver
- Mushrooms
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant known for its protective effects against inflammation and oxidative stress. In the skin, for example, vitamin E helps relieve rashes, redness and similar forms of skin inflammation. Vitamin E also helps protect the skin from ultraviolet light-induced damage.
Additionally, vitamin E protects the eyes from damage caused by inflammation. This damage could otherwise lead to the formation of cataracts and the development of age-related macular degeneration, a leading cause of vision loss.
These foods provide ample amounts of vitamin E:
- Chia seeds
- Hazelnuts
- Peanuts
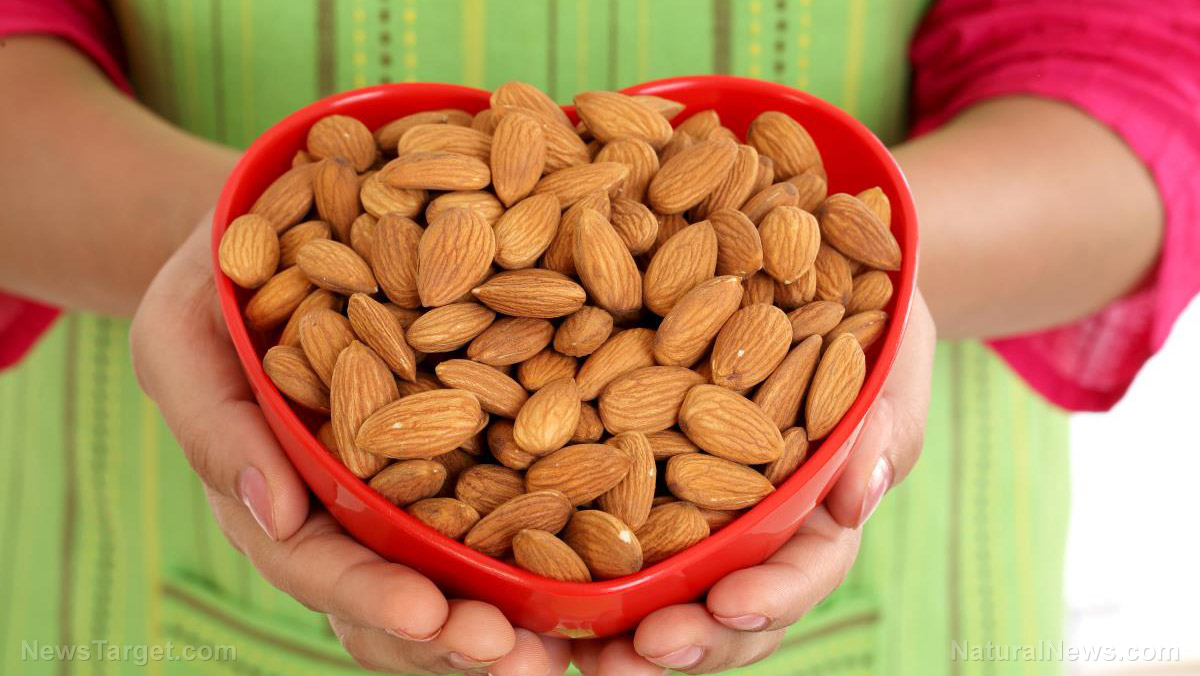
- Almonds
- Avocado
- Spinach
- Broccoli
Vitamin K
Vitamin K inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby protecting against inflammation. For this reason, maintaining healthy levels of vitamin K is thought to positively influence chronic disease risk.
Vitamin K is found in two natural forms: phylloquinone (vitamin K1) and menaquinone (vitamin K2). The following foods contain either form of vitamin K:
- Kale
- Spinach
- Broccoli
- Cabbage
- Chicken
- Liver
- Eggs
B vitamins
B vitamins, particularly B6 and B9, also help reduce CRP levels of CRP in the blood. In fact, some studies show that people with low vitamin B6 levels will often have high levels of CRP, indicating inflammation. Meanwhile, other studies suggest that daily supplementation with folic acid, or vitamin B9, may help reduce inflammation.
These foods contain at least one essential B vitamin:
- Green leafy vegetables
- Black-eyed peas
- Beef liver
- Asparagus
To fight chronic inflammation, eat a healthy diet containing foods rich in the vitamins listed above.
Learn more about anti-inflammatory vitamins at Nutrients.news.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 SUPERFOODS NEWS