Supplementing with green cardamom improves biomarker for NAFLD in obese patients
09/04/2019 / By Melissa Smith
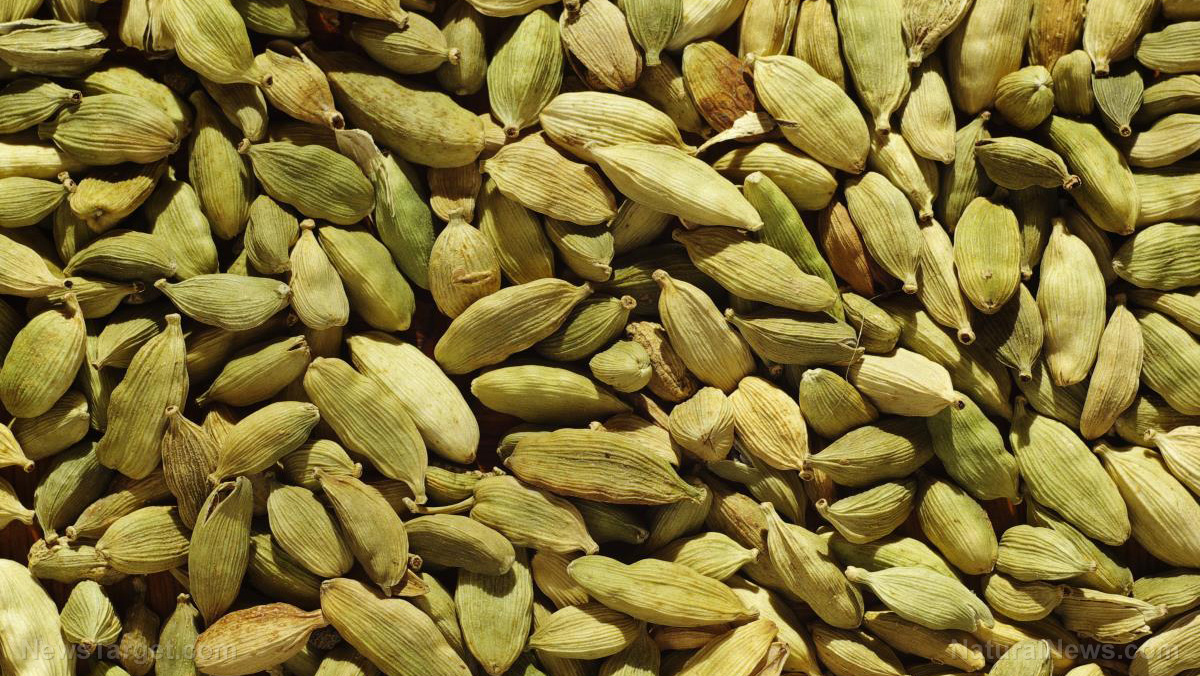

A team of researchers from Tehran, Iran looked at the ability of green cardamom supplementation on improving NAFLD biomarkers in overweight or obese patients. The team published their findings in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a common form of liver disease that is not caused by alcohol consumption.
- The researchers examined the effects of green cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum) on serum glucose indices, lipids, and irisin level in overweight or obese people with NAFLD.
- They recruited 87 participants and randomly divided them into two groups: a green cardamom treatment group and a placebo group.
- Participants in the green cardamom group received 500 mg of green cardamom capsules thrice a day with meals for three months.
- The researchers also measured the participants’ levels of fasting blood sugar, insulin, total cholesterol, triglyceride, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol.
- They also measured the levels of irisin, myokine and adipokine that can influence insulin sensitivity.
- The participants’ insulin sensitivity and insulin resistance were also measured.
- The results showed that participants who received green cardamom supplementation significantly increased irisin, HDL cholesterol, and insulin sensitivity.
- Supplementing with green cardamom also reduced fasting blood sugar, triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, insulin resistance, and the grade of fatty liver.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that green cardamom supplementation can be beneficial for overweight or obese people with NAFLD.
Read the full text of the study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Daneshi-Maskooni M, Keshavarz SA, Qorbani M, Mansouri S, Alavian SM, Badri-Fariman M, Jazayeri-Tehrani SA, Sotoudeh G. GREEN CARDAMOM SUPPLEMENTATION IMPROVES SERUM IRISIN, GLUCOSE INDICES, AND LIPID PROFILES IN OVERWEIGHT OR OBESE NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE PATIENTS: A DOUBLE-BLIND RANDOMIZED PLACEBO-CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 12 March 2019; 19(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-019-2465-0
Tagged Under:
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 SUPERFOODS NEWS