Condensed tannins from the miracle tree found to have therapeutic effects against chronic diseases, including cancer
10/15/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez

Interest in plant-derived compounds has not waned for the past several years but, instead, has grown enormously. Researchers continue to study plants and their chemical components due to their advantages over pharmaceutical drugs. Not only do phytochemicals show more effectiveness than modern medications, they also cause less toxicity to the body and produce very few side effects. One example of plant compounds with health-promoting qualities are condensed tannins. According to researchers from the Universiti Putra Malaysia, condensed tannins from the “miracle tree” Leucaena leucocephala hybrid-Rendang have biological activities that may be useful for treating various diseases. In their study published in the journal Food Science and Human Wellness, they reported that these compounds can be used as potent antioxidant, anti-microbial, and anti-cancer agents.
Extracts from the miracle tree show promise as potential treatment for inflammatory-related diseases
L. leucocephala hybrid-Rendang can be found in abundance in Malaysia. This tree is a hybrid of two species, namely, L. leucocephala and L. diversifolia, and is used for a variety of things, including as a protein supplement for animals. L. leucocephala hybrid-Rendang is rich in condensed tannins or proanthocyanidins, a class of medicinal plant compounds known for their antioxidant activities. Proanthocyanidins are also credited with possessing anti-inflammatory, anti-asthmatic, anti-cancer, antiviral, anti-allergic, anti-microbial, and anti-hypertensive properties.
The health benefits of condensed tannins are wide-ranging. According to multiple studies, these compounds can:
- Promote wound healing
- Relieve pain caused by pancreatitis
- Reduce insulin resistance in diabetics
- Protect from drug toxicity
- Decrease low-density lipoproteins (LDL) in the blood
- Prevent LDL oxidation, which can lead to atherosclerosis
For their study, the researchers investigated the biological activities of condensed tannins found in L. leucocephala hybrid-Rendang. They focused mainly on their antioxidant, anti-microbial, and anti-cancer capabilities as these are the least explored. After subjecting L. leucocephala hybrid-Rendang extracts to three different assays, the researchers found that they possessed high free radical-scavenging activities. The extracts containing condensed tannins also showed anti-microbial potency against various strains of Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria.
The researchers tested the cytotoxicity of the extracts on different cancer cells lines. These included human breast adenocarcinoma (MCF-7), human colon carcinoma (HT29), human cervical carcinoma (HeLa), and human liver carcinoma (HepG2) cells. They reported that among these cell lines, the condensed tannins from L. leucocephala hybrid-Rendang showed the highest effectiveness against MCF-7 cells. The researchers observed cell shrinkage, nuclear condensation, and the formation of apoptotic bodies, which are all characteristic of apoptosis, after treating MCF-7 with L. leucocephala hybrid-Rendang extracts.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that CTs can be used as an alternative treatment for various oxidative and inflammatory diseases.
Great food sources of condensed tannins
Proanthocyanidins are flavonoid oligomers, meaning that their structures consist of a few repeating units. These smaller units are also known for their beneficial properties. For instance, flavan-3-ols like catechins, epicathechins, and gallocatechins, which are phytonutrients found in red wine and tea, are structural components of proanthocyanidins. (Related: Grape seed flavonoids demonstrate anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.)
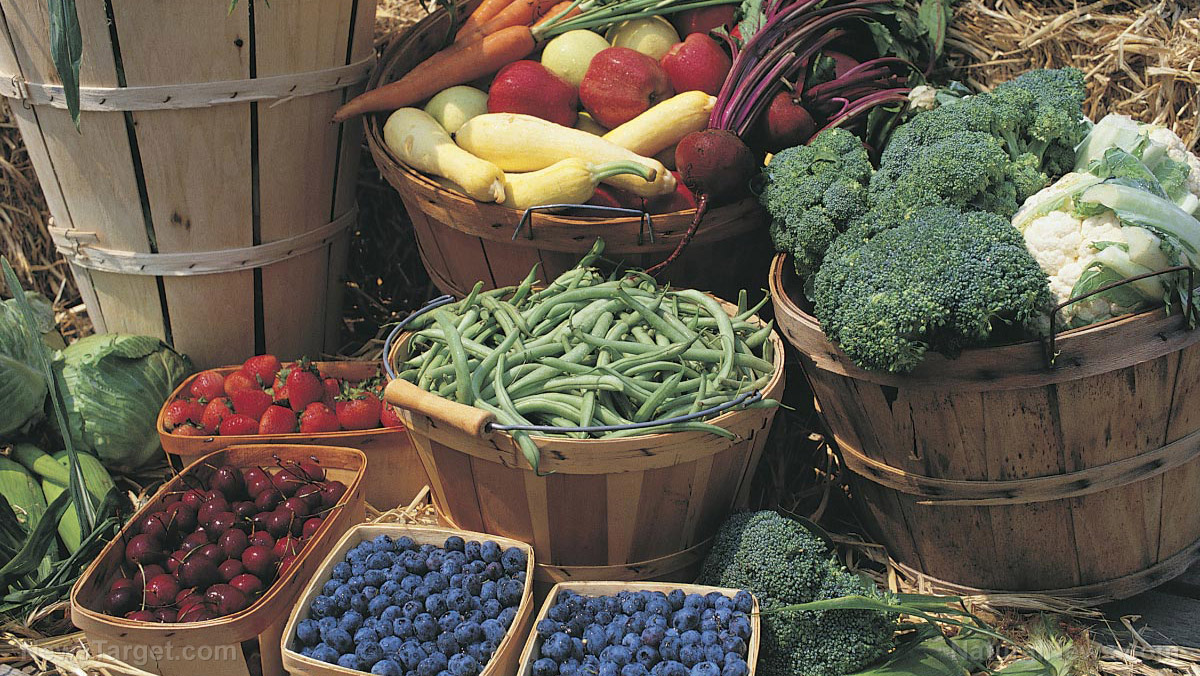
Proanthocyanidins are widely distributed in plants and can, therefore, be sourced from plant-based foods. Some common (and abundant) food sources of condensed tannins include:
- Apples
- Barley
- Bilberries
- Birch
- Black grapes
- Blueberries
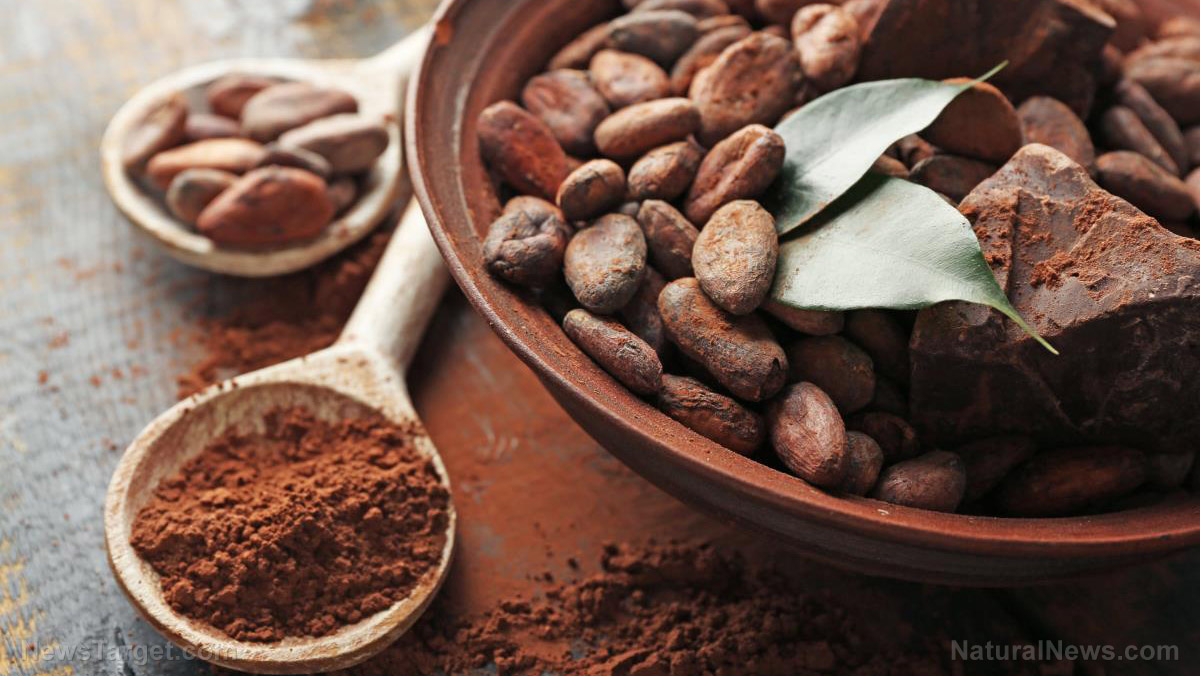
- Chocolate
- Cocoa
- Coffee
- Cranberries
- Ginkgo biloba
- Grape seeds
- Green grapes
- Legumes
- Nuts
- Pine bark
- Red cabbage
- Red grapes
Proanthocyanidins can protect the body against oxidative stress and inflammation-related diseases like heart disease and cancer. To gain the health benefits of these compounds, incorporate foods rich in proanthocyanidins into your diet.
Sources include:
Tagged Under:
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 SUPERFOODS NEWS