Shiitake and MCT-rich plant oil can reduce the effects of a high-fat diet
12/10/2018 / By Edsel Cook
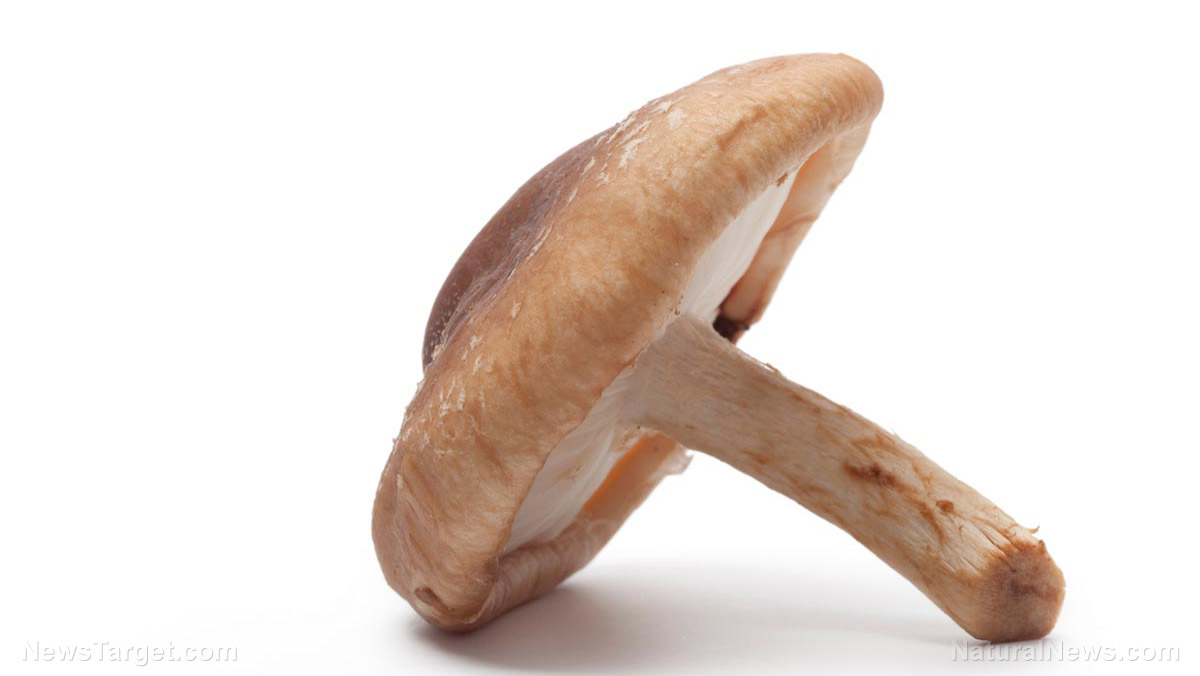

The eritadenine found in shiitake mushrooms (Lentinula edodes) is known to lower cholesterol levels and helps produce the essential amino acid methionine. Japanese researchers reported that shiitake supplements could improve the serum lipid concentrations of rats given fatty diets with different kinds of lipids.
Their research effort was supported by Beppu University. They published their paper in the Journal of Dietary Supplements.
- The animals in the rat model were divided according to diet. They were given either a plant oil-based diet, another plant oil diet that was rich in medium-chain triglycerides (MCT), and an animal fat-based diet of lard. Some of the animals in each group also received shiitake extract.
- At the end of the trial, the animals were sacrificed. Blood samples were analyzed for serum lipid profiles and lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) activities.
- Rats that received shiitake supplements demonstrated lower serum triglyceride, cholesterol, and LCAT activity compared to those that didn’t get any. The supplemented rats with the MCT-rich plant oil diet demonstrated more significant improvements than those that subsisted on lard.
- The serum cholesterol and LCAT were affected by the type of lipid in the diet. Animals given plant oils showed much lower levels of the two, and the ones fed MCT-rich food were better off than their non-MCT-rich counterparts.
- Shiitake and MCT-rich plant oil appeared to complement each other. Animals that got both had demonstrated the best serum lipid profiles and LCAT activities.
The researchers concluded that the eritadenine in shiitake can break down both plant and animal fats and that its hypocholesterolemic activity works better if paired with plant oils rich in medium-chain triglyceride.
Learn about the other health benefits that come from eating shiitake at SuperFoodNews.com.
Journal Reference:
Asada N, Kairiku R, Tobo M, Ono A. EFFECTS OF SHIITAKE INTAKE ON SERUM LIPIDS IN RATS FED DIFFERENT HIGH-OIL OR HIGH-FAT DIETS. Journal of Dietary Supplements. 2018 Apr 27:1–12. DOI: 10.1080/19390211.2018.1458768.
Tagged Under: